AFPSAT Courses
The AFPSAT Exam caters for (3) three major subtests which consists of the following:
- Abstract Reasoning
- Verbal Reasoning
- Numerical Reasoning
What is Abstract Reasoning?
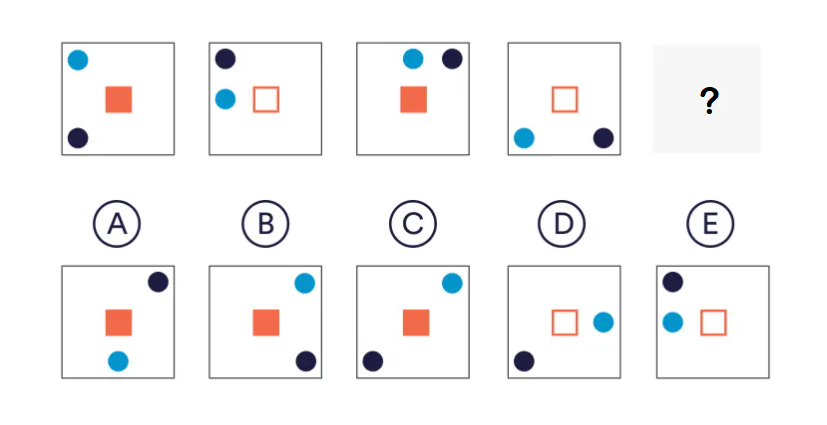
Abstract Reasoning is most closely related to fluid intelligence: our ability to quickly reason with information to solve new, unfamiliar problems, independent of any prior knowledge (which is very important in the military). It includes lateral and flexible thinking, logical reasoning, and generating solutions beyond the most obvious. Someone who is strong in Abstract Reasoning would be able to use logic to extrapolate rules or relationships to other possible extreme scenarios.
Abstract Reasoning items involve shapes and patterns. You may also hear these tests referred to as ‘Logical’ or ‘Inductive’ Reasoning assessments.
They generally involve figuring out the ‘underlying rule’ in a given sequence or pattern and then applying this rule to solve a problem. It does not really matter whether the given pattern is made up of symbols, shapes, or numbers; it is just ‘new data’ to be interpreted.
What is Verbal Reasoning?

Verbal reasoning is a cognitive ability that involves understanding, analyzing, and drawing conclusions from written or spoken language. It encompasses the ability to comprehend and manipulate information presented in words, texts, or verbal statements. Verbal reasoning skills often involve tasks such as understanding written passages, identifying relationships between words, deducing conclusions from arguments, and evaluating the validity of statements.
In summary, verbal reasoning is important because it underlies various aspects of cognitive and social functioning. It is a foundational skill that supports success in education, career, and daily life by enhancing communication, critical thinking, and problem-solving abilities.
What is Numerical Resoning?

Numerical reasoning refers to the ability to understand, interpret, and analyze numerical information in various forms, such as tables, charts, graphs, and mathematical problems. It involves basic arithmetic, data analysis, and logical reasoning skills to draw meaningful conclusions from numerical data.
Improving numerical reasoning skills often involves practice, exposure to various types of numerical data, and developing a solid foundation in basic mathematical concepts. Employers, educators, and individuals recognize the importance of numerical reasoning in navigating the challenges of the modern world.